A look at the most significant changes due to hit Microsoft’s evolving OS in the coming year.

Microsoft has made many promises about what Windows 10 will do, and while some have materialized, others still remain ambitions.
As a perpetual work-in-progress, Windows 10 continues to accrue new features, as Windows catches up with Microsoft’s vision of it being an OS that runs anywhere, syncs with the cloud and has an intelligent assistant at its core.
While Windows 10 will be buffed up by the arrival of the Windows 10 Creators Update early next year, 2017 as a whole will see the OS undergo significant changes, some of which are long-awaited. Here’s what to look out for.
Windows 10 phones edge closer to replacing desktop PCs
Microsoft has long pushed the idea that Windows 10 on phones will be so powerful, it’ll be akin to carrying a full PC in your pocket, courtesy of the OS’ Continuum feature.
“With Continuum for phones, we believe that any screen can be your PC,” Joe Belfiore, Microsoft’s corporate VP of the operating systems group, told the Microsoft Build Developer Conference in 2015, going on to add:
“Imagine the effect this could have on mobile first countries, where individuals could be as effective with the phone that they’re buying.”
Today the reality of using Continuum on Windows 10 falls somewhat short of Belfiore’s future-gazing. While a select Windows 10 phones, such as the Lumia 950, can be hooked up to mouse, keyboard and monitor and used as a Windows desktop there are significant limitations. Only one fullscreen app can be used at a time, legacy Windows apps won’t run on existing handsets and even Universal Windows Platform apps need to explicitly support Continuum.
However, in addition to the possibility of legacy apps running on smartphones, see below, various improvements to Continuum are due to land with the Creators Update in early 2017.
These include support for more PC features, such as running multiple Windows side-by-side on the desktop, pinning apps to the Taskbar and hitting the Windows button to bring up the search box. Other improvements include the ability to keep your phone in your pocket and have it connect wirelessly to a docking station and to independently customize the Windows Start screen on the phone display and on a PC monitor.
Running classic Windows software on your phone
This one’s a rumor but based on solid foundations, and with the potential to transform Windows 10’s appeal on mobile if correct.
The big fly in the ointment when it comes to using Windows 10’s Continuum feature to run a phone as a PC is that Windows 10 phones only run Universal Windows Platform apps. This incompatibility means that widely-used Windows apps from desktop PCs can’t be used on handsets.
However, by sniffing around inside Windows 10’s code, users have uncovered signs that Microsoft is working on bringing these apps to Windows phones.
The code in question suggests that Microsoft is building an emulator that would allow desktop x86 apps to work on the ARM64-based handsets.
As reported by ZDNet’s Mary Jo Foley last month, Twitter user WalkingCat found a reference to what he termed “Windows’s hybrid x86-on-ARM64 tech” in Windows’ codebase, which also referenced the term, “CHPE.”
The clue chimed with Foley, who said her sources had told her that Windows 10 will gain this x86 on ARM64 emulation capability, but not until Fall 2017.
Foley guesses that C stands for Cobalt, the codename for x86 emulation on ARM, and that HP relates to the tech giant HP, which has been working with Microsoft on its the HP Elite x3 Windows Phone, a Windows 10 handset that can serve as a desktop PC via Continuum.
Microsoft certainly has good reasons for wanting such emulation to work. If Windows 10 phones could run as Windows desktops with full support for legacy apps, without having to resort to remote desktop software, Windows 10 phones could suddenly be far more appealing to business.
Return of OneDrive placeholders
Since the launch of Windows 10, many users have been petitioning Microsoft to reintroduce placeholders to the OS’ built-in OneDrive cloud storage service.
In Windows 8.1, placeholders, also called smart files, let users see all of their files stored on OneDrive, whether those files were stored on the device or not.
This feature was removed from Windows 10 but is now due to be bought back in Windows 10 File Explorer when browsing OneDrive. The returning feature will work in a similar fashion to Windows 8.1’s placeholders, showing users files both stored locally and on OneDrive, allowing them to download files and folders to the device and keep them in sync with OneDrive.
Orchestrate Windows apps using Linux tools
Microsoft recently updated Windows 10 to let users run a range of Linux tools from inside the OSand seems committed to continuing to improve support for Linux command-line software in Windows.
In Windows 10, Ubuntu/Linux software runs on top of the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Users run Linux software and issue commands at the command line via the Bash shell.
Microsoft is working to increase the range of commands that can be run via the shell but perhaps the most significant change on the horizon is increased interoperability between the Bash and Windows environments. Effectively this will let developers call Windows applications from within Bash — allowing them to write a Bash script to automate a complex build that includes Windows applications — and to invoke Bash applications from Windows PowerShell.
These changes will be generally available in Windows 10 after the Creators Update early next year.
Easy communication with friends and family
Next year’s Creators Update will boost Windows 10’s social credentials, with a series of changes to make it simpler to stay in touch and share content with friends and family.
The Windows MyPeople feature will allow users to pin their favorite contacts to the right-hand side of Windows taskbar. Clicking on a pinned contact’s face brings up email or Skype messages from only that person and files can be dragged files to that person’s face for quick sharing. Informal check-ins also become easier, with the Shoulder Taps feature allowing pinned contacts to send friends animated emojis and other clipart, which pop up above that contact’s face on the taskbar.
Focusing Windows around virtual and augmented reality
Microsoft plans to put 3D and virtual reality at the heart of Windows 10, as it bets on the success of low-cost headsets due out next year.
Acer, Asus, Dell, HP and Lenovo will release virtual reality head-mounted displays, with prices starting from $299.
Some of these headsets will be released in March, to coincide with the release of the Windows 10 Creators Update, which will include various tools to simplify the creation and sharing of 3D content, including a new version of Microsoft Paint.
In a demo earlier this year, Microsoft showed how Windows 10 could work on virtual reality headsets, demonstrating a mock-up of a virtual space with a large TV screen and virtual shelves stocked with apps and 3D models, and with the Edge browser appearing as a large window in the wearer’s view.
Another demo, this time using the far more expensive Microsoft HoloLens, showed Microsoft’s Edge browser as a window in the user’s vision, from which the demoer dropped actual-sized 3D models of stools from the furniture site Houzz around the room, in order to see what they looked like in real life.
Allowing Windows to function in this way is Windows Holographic, a variant of the Microsoft OS that provides a platform for virtual and augmented reality headsets to run Universal Windows Platform apps.
More detail on Microsoft’s VR and AR plans are expected this week at the WinHEC conference in China.
Better battery life
Windows 10 PCs and tablets should have better battery life after the Creators Update lands in March, thanks to changes to how the OS is patched.
The steady stream of updates isn’t going to slow down but they are going to suck up less bandwidth and reduce strain on phone and laptop batteries.
Download sizes for major updates will be cut by about 35 percent and battery life of Windows 10 mobile devices will improve, due to each device spending less time checking for updates.
The improvements will stem from Windows 10’s new Unified Update Platform, already used for Windows 10 on phones, which only updates each device with the files it needs, rather than delivering all updates to date, and doesn’t rely so heavily on the user’s device to process update data.
Windows Defender Application Guard
Coming to Windows 10 Enterprise users early next year, Windows Defender Application Guard is designed to help protect firms against online threats.
The new safeguard will add container-based isolation to Windows 10’s Edge browser.
Application Guard will ensure that when Edge accesses a website not designated as trusted, the browser will be launched inside a container, a virtualized environment isolated from the rest of the Windows OS.
If the site tries to download and run malicious code on the device, that code remains within the container, unable to permanently compromise the Windows device or the wider network, and disappears when the browser session shuts down.
Unlike the software-based sandboxes that are offered by other browsers, Microsoft says that Application Guard provides a hardware-based container that offers greater protection to the device.
Other enterprise-focused changes in the forthcoming Creators Update include improvements to Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection’s ability to detect and respond to network attacks, an upgrade to the Windows Analytics dashboard to display additional information about the composition of IT estates, a new tool for in-place UEFI conversion, and a mobile application management feature for protecting data on employees’ personal devices.
Home Hub
Rather than building hardware to challenge voice-controlled virtual assistants such as Amazon Echo and Google Home, it seems as if Microsoft is working on transforming Windows 10 into what it calls a Home Hub.
Evidence of this shift comes from a Windows Central interview with unnamed sources. These sources claim that Home Hub will turn Windows into a shared computing environment for the home, allowing family members to more easily share calendars, apps and services.
A future-gazing Microsoft video from 2013, dug out by ZDNet’s Mary Jo Foley, shows how this system might eventually work. In it, family members share access to photos, apps and calendars on a screen attached to a wall and interact with computers around the home, for example scanning carrots to find appropriate recipes. Adding credence to the Home Hub rumor are references to Home Hub being a shared family account in Windows 10, as discovered by Twitter user WalkingCat.
ZDNet’s Foley also references a recent Microsoft job posting for a software engineer in the Windows and Devices Group, which is seeking someone to expand Windows’ “family” credentials.
According to the ad, this engineer will play a critical role in helping families to “share pictures, videos, applications, games, and other purchases easily” and to “communicate freely and stay in touch” using Windows 10.
Blue light reduction
One more unconfirmed new feature appears to be aimed at helping Windows 10 users get a good night’s sleep.
Being exposed to blue light from computer screens late at night can supposedly disrupt the body’s sleep cycle.
To counter this disturbance, Windows 10 already has f.lux software that reduces blue light emitted by screens close to bedtime.
But it seems that Microsoft may be working on its own feature to address the issue.
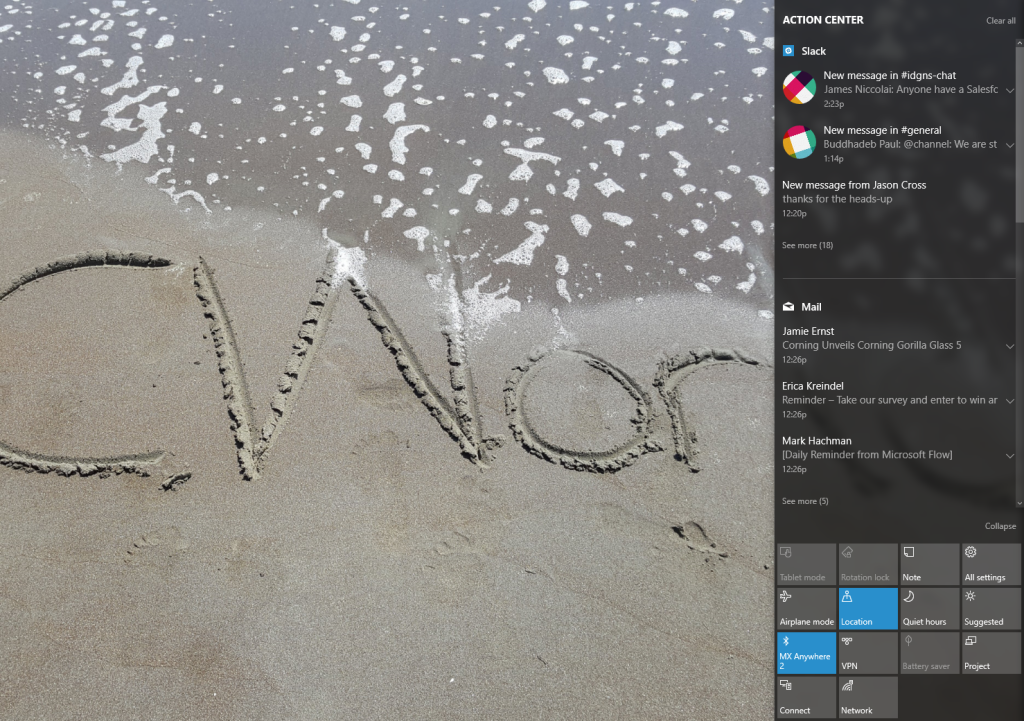
Twitter user Core has discovered references to “BlueLightReduction” hidden within early builds of the OS being tested under the Windows Insider Program, a setting which appears as if would be toggled from Windows 10’s Action Center.
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsofts Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.