New features make Office and OneDrive the best place to work on iPad and iPhone

More and more, people around the world are working on the go, changing locations and devices as they create and collaborate with others throughout their day. As they work across their PCs, Macs and mobile devices, they expect an uncompromising experience that is familiar yet optimized for the device they are using.
Microsoft is committed to providing best in class experiences on all devices, and today, we are proud to share with you a set of new Office capabilities across Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and OneDrive on iOS that will delight and make iPad and iPhone users more productive than ever before.
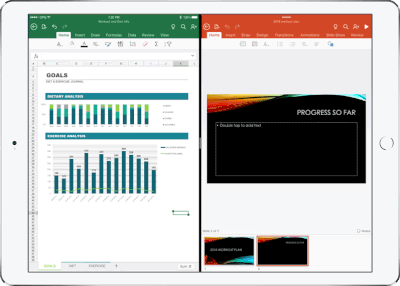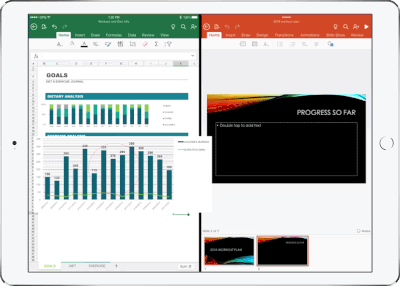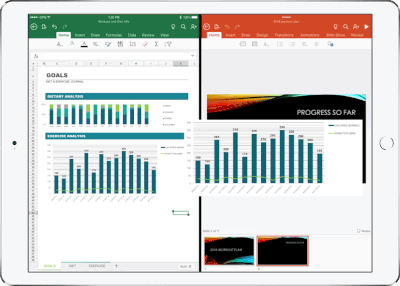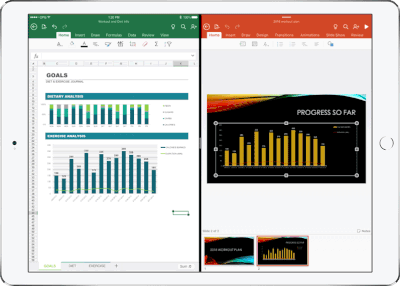
Real-time co-authoring in Word, Excel, and PowerPoint on iOS – We live in a world where we’re often collaborating with multiple people in different locations and Office 365 provides the broadest and deepest toolkit for collaboration between individuals, teams, and entire organizations. Using real-time co-authoring, colleagues, friends, and family can contribute to and edit documents simultaneously in the Word, Excel and PowerPoint iOS apps. This allows you to know who else is working with you in a document, see where they’re working, and view changes automatically within seconds. The co-authoring experiences are also available in Office Online and the latest versions of Word, Excel and PowerPoint on the PC and Mac, all made possible by storing your documents in OneDrive or SharePoint.
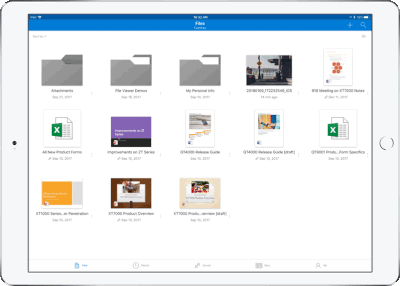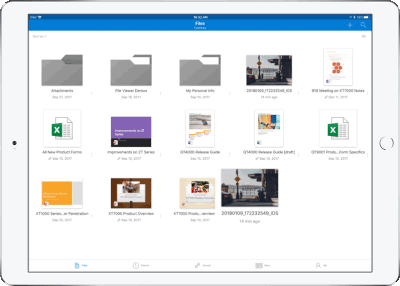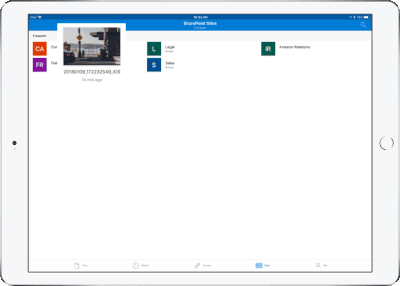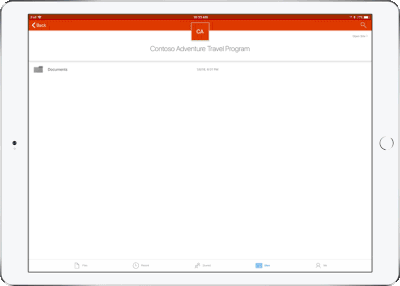
Drag and drop files anywhere with OneDrive – Sometimes your files can get scattered between different folders or even services and applications. Now it’s easier than ever to organize and rearrange your files. You can drag files in between folders in OneDrive and, if your teammates use SharePoint to work together, you can even drag OneDrive files to a SharePoint site giving them immediate access. On iPad, you can also drag files from other apps, such as iMessage, into your OneDrive and drag files out of your OneDrive to other apps.
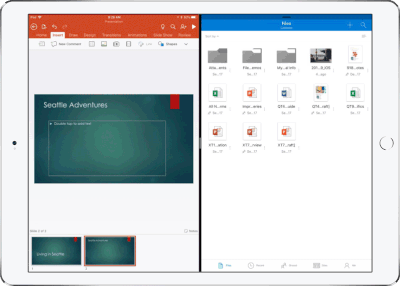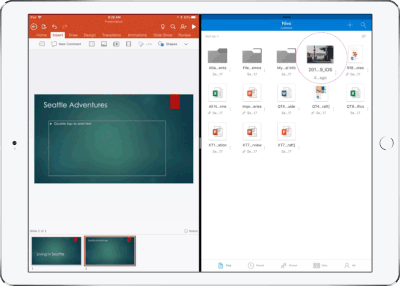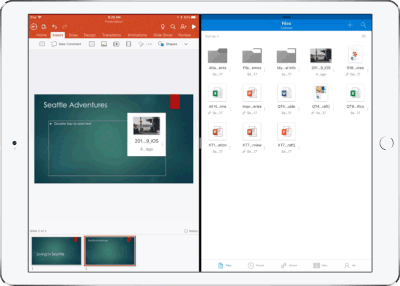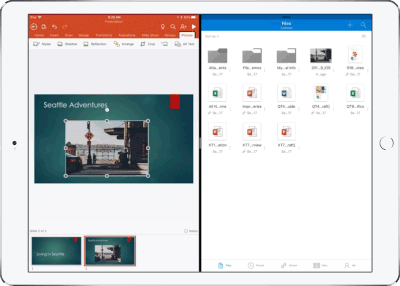
Drag and drop content between Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and OneDrive on iPad – One of the most common and powerful tasks when creating content is pulling in text, photos, graphs, and other objects from different sources. Now you can pull in content with ease on your iPad with drag and drop support in Office and OneDrive. Easily drag and drop objects from OneDrive or from one Office app to another.
OneDrive Files app support – Today we’re also announcing native support for the Files app in iOS 11. OneDrive integration with the Files app allows you to access, upload, edit, and save your content to OneDrive or SharePoint from apps that support Files app integration. You can also tag and favorite your OneDrive and SharePoint files from within the Files app.
OneDrive redesigned to find the files that matter – The OneDrive iOS app has been redesigned from the ground up with a new layout that uses your screen space more efficiently allowing you to find your files faster. It’s easier to scan across file names, see the information that matters to you, and sort files how you want. New metadata is visible in the list view, so you can easily identify new files and files that have been shared.

Universal link support for shared files – Being able to seamlessly share and securely access files is essential for teamwork. Previously when you received a link to a shared file, you would be directed to a browser and prompted to re-authenticate. Today, we are announcing universal link support, which will open the document directly in the Word, Excel, or PowerPoint iOS apps. Further, if you don’t have a supporting application for the file, you’ll be directed to the OneDrive app to preview the file.
Preview 130+ file types in your OneDrive app – You and the people you work with use a variety of different file formats, but when you’re on your mobile device you might not have access to the native applications for those files. Now, the OneDrive iOS app creates crisp thumbnails and supports large previews of over 130 file types, including Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator, RAW, 3D objects, and high-precision DICOM images. OneDrive lets you open, view, and share all of your files without leaving the app.
New accessibility features for Word, Excel and PowerPoint on iOS 11
The VoiceOver rotor in iOS improves navigation and the accessibility of content. For example, you can use the built-in rotor on iOS to navigate line-by-line or word-by-word and change the speed at which VoiceOver speaks. The new Office-specific rotors also let people with vision impairments navigate more efficiently in Word across tables and links, slides in PowerPoint, and sheets in Excel.
Users can also leverage larger text options in accessibility settings to modify the text size in the core Office apps. Visit the support pages for Excel, Word, and PowerPoint to learn more.
You can use take advantage of these new capabilities in the coming days by updating the Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and OneDrive apps in the Apple App Store.

![]()
![]()