Want Windows 10 to run faster? Take a few minutes to try out these tips, and your machine will be zippier and less prone to performance and system issues.

1. Change your power settings
If you’re using Windows 10’s Power saver plan, you’re slowing down your PC. That plan reduces your PC’s performance in order to save energy. (Even desktop PCs typically have a Power saver plan.) Changing your power plan from Power saver to High performance or Balanced will give you an instant performance boost.
To do it, launch Control Panel, then select Hardware and Sound > Power Options. You’ll typically see two options: Balanced (recommended) and Power saver. (Depending on your make and model, you might see other plans here as well, including some branded by the manufacturer.) To see the High performance setting, click the down arrow by Show additional plans.
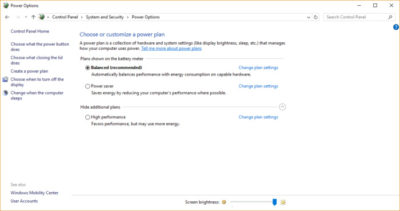
To change your power setting, simply choose the one you want, then exit Control Panel. High performance gives you the most oomph, but uses the most power; Balanced finds a median between power use and better performance; and Power saver does everything it can to give you as much battery life as possible. Desktop users have no reason to choose Power saver, and even laptop users should consider the Balanced option when unplugged and High performance when connected to a power source.
2. Disable programs that run on startup
One reason your Windows 10 PC may feel sluggish is you’ve got too many programs running in the background programs that you may never use, or only rarely use. Stop them from running, and your PC will run more smoothly.
Start by launching the Task Manager: Press Ctrl-Shift-Esc or right-click the lower-right corner of your screen and select Task Manager. If the Task Manager launches as a compact app with no tabs, click “More details” at the bottom of your screen. The Task Manager will then appear in all of its full-tabbed glory. There’s plenty you can do with it, but we’re going to focus only on killing unnecessary programs that run at startup.
Click the Startup tab. You’ll see a list of the programs and services that launch when you start Windows. Included on the list is each program’s name as well as its publisher, whether it’s enabled to run on startup, and its “Startup impact,” which is how much it slows down Windows 10 when the system starts up.
To stop a program or service from launching at startup, right-click it and select “Disable.” This doesn’t disable the program entirely; it only prevents it from launching at startup — you can always run the application after launch. Also, if you later decide you want it to launch at startup, you can just return to this area of the Task Manager, right-click the application and select “Enable.”
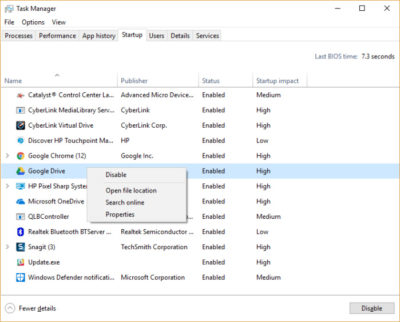
Many of the programs and services that run on startup may be familiar to you, like OneDrive or Evernote Clipper. But you may not recognize many of them. (Anyone who immediately knows what “bzbui.exe” is, please raise your hand. No fair Googling it first.)
The Task Manager helps you get information about unfamiliar programs. Right-click an item and select Properties for more information about it, including its location on your hard disk, whether it has a digital signature, and other information such as the version number, the file size and the last time it was modified.
You can also right-click the item and select “Open file location.” That opens File Explorer and takes it to the folder where the file is located, which may give you another clue about the program’s purpose.
Finally, and most helpfully, you can select “Search online” after you right-click. Bing will then launch with links to sites with information about the program or service.
If you’re really nervous about one of the listed applications, you can go to a site run by Reason Software called Should I Block It? and search for the file name. You’ll usually find very solid information about the program or service.
Now that you’ve selected all the programs that you want to disable at startup, the next time you restart your computer, the system will be a lot less concerned with unnecessary program.
3. Turn off search indexing
Windows 10 indexes your hard disk in the background, allowing you – in theory – to search your PC more quickly than if no indexing were being done. But slower PCs that use indexing can see a performance hit, and you can give them a speed boost by turning off indexing. Even if you have an SSD disk, turning off indexing can improve your speed as well, because the constant writing to disk that indexing does can eventually slow down SSDs.
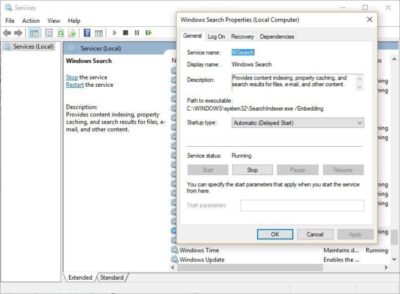
To get the maximum benefit in Windows 10, you need to turn indexing off completely. To do so, first type services.msc in the Start Menu search box, and click the Services result that come up. The Services app then appears. Scroll down to either Indexing Service or Windows Search in the list of services. Double-click it, and from the screen that appears, click Stop. Then reboot. Your searches may be slightly slower, although you may not notice the difference. But you should get an overall performance boost.
If you’d like, you can turn off indexing for only files in certain locations. To do this, first type index in the Start Menu search box, and click the Indexing Options result that appears. The Indexing Options page of Control Panel appears. Click the Modify button and you’ll see a list of locations that are being indexed, such as Microsoft Outlook, your personal files, and so on. Uncheck the boxes next to any location, and it will no longer be indexed.
4. Clean out your hard disk
If you’ve got a bloated hard disk filled with files you don’t need, you could be slowing down your PC. Cleaning it out can give you a speed boost. Windows 10 has a surprisingly useful built-in tool for doing this called Storage Sense. Go to Settings > System > Storage and at the top of the screen – in the Storage Sense section – move the toggle from Off to On. When you do this, Windows constantly monitors your PC, and deletes old junk files you no longer need; temporary files; files in the Downloads folder that haven’t been changed in a month; and old Recycle Bin files.
You can customize how Storage Sense works and also use it to free up even more space than it normally would. Underneath Storage Sense, click “Change how we free up space automatically.” From the screen that appears, you can change how often Storage Sense deletes files (every day, every week, every month or when Windows decides). You can also tell Storage Sense to delete files in your Download folder, depending on how long they’ve been there. And you can also set how long to wait to delete files in the Recycle Bin automatically.
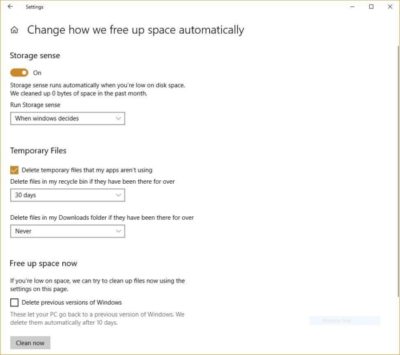
You can also delete old versions of Windows that might be hogging space. At the bottom of the screen, check the box next to “Delete previous versions of Windows.” Storage Sense will then delete old versions of Windows ten days after you’ve installed an upgrade. Note that if you do this, you won’t be able to revert to the older version of Windows.
5. Clean out your Registry
Under the Windows hood, the Registry tracks and controls just about everything about the way Windows works and looks. That includes information about where your programs are stored, which DLLs they use and share, what file types should be opened by which program or just about everything else.
But the Registry is a very messy thing. When you uninstall a program, for example, that program’s settings don’t always get cleaned up in the Registry. So over time, it can get filled with countless outdated settings of all types. And that can lead to system slowdowns.
Don’t even think of trying to clean any of this out yourself. It’s impossible. To do it, you need a Registry Cleaner. There are plenty available, some free and some paid. But there’s really no need to outright buy one, because the free Auslogics Registry Cleaner does a solid job.
Before using Auslogics or any other Registry Cleaner, you should back up your Registry so you can restore it if anything goes wrong. (Auslogics Registry Cleaner does this for you as well, but it can’t hurt to have it backed up twice.) To do your own Registry backup, type regedit.ext in the search box, then press Enter. That runs the Registry editor. From the File menu, select Export. From the screen that appears, make sure to choose the “All” option in the Export range section at the bottom of the screen. Then choose a file location and file name and click Save. To restore the Registry, open the Registry editor, select Import from the File menu, then open the file you saved.
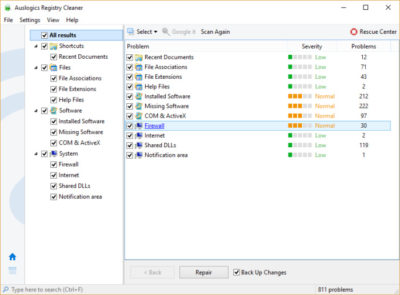
Now download, install and run Auslogics Registry Cleaner. On the left-hand side of the screen you can select the kinds of Registry issues you want to clean up – for example, File Associations, Internet or Fonts. I generally select them all.
Next tell it to scan the Registry for problems. To do that, click “Scan Now” and from a drop-down menu that appears select Scan. That lets you first examine the Registry problems it finds. If you instead choose “Scan and Repair,” it makes the fixes without you checking them.
It now scans your Registry for errors, then shows you what it found. It ranks the errors according to their severity, to help you decide which to fix. Click Repair when you’ve made your decision, and make sure that “Back up Changes” is checked, so you can restore the Registry easily if something goes wrong.
6. Disable shadows, animations and visual effects
Windows 10 has some nice eye candy — shadows, animations and visual effects. On fast, newer PCs, these don’t usually affect system performance. But on slower and older PCs, they can exact a performance hit.
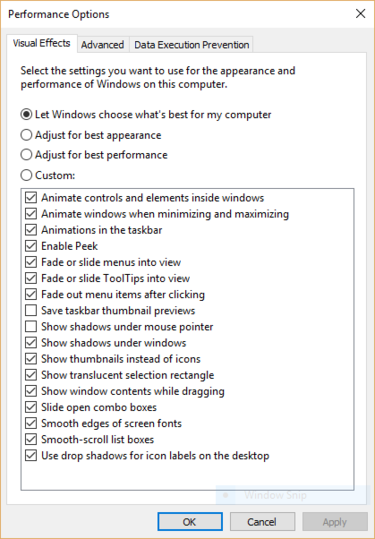
It’s easy to turn them off. In the Windows 10 search box type sysdm.cpl and press Enter. That launches the System Properties dialog box. Click the Advanced tab and click “Settings” in the Performance section. That brings you to the Performance Options dialog box. You’ll see a varied list of animations and special effects.
If you have time on your hands and love to tweak, you can turn individual ones on and off. These are the animations and special effects you’ll probably want to turn off, because they have the greatest effect on system performance:
- Animate controls and elements inside windows
- Animate windows when minimizing and maximizing
- Animations in the taskbar
- Fade or slide menus into view
- Fade or slide ToolTips into view
- Fade out menu items after clicking
- Show shadows under windows
However, it’s probably a lot easier to just select “Adjust for best performance” at the top of the screen and then click OK. Windows 10 will then turn off the effects that slow down your system.
7. Launch the Windows troubleshooter
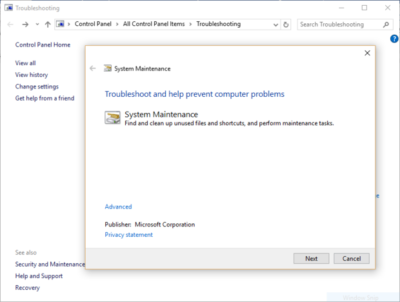
Windows 10 has a very useful, little-known tool that can sniff out performance problems and solve them. To launch it, run Control Panel and select System and Security > Security and Maintenance > Troubleshooting > Run maintenance tasks. A screen titled “Troubleshoot and help prevent computer problems” will appear. Click Next.
The troubleshooter will find files and shortcuts you don’t use, identify any performance and other issues on your PC, report them to you and then fix them. Note that you may get a message that says, “Try troubleshooting as an administrator.” If you have administrative rights to the PC, click it and the troubleshooter will launch and do its work.
8. Get help from the Performance Monitor
There’s a great tool in Windows 10 called the Performance Monitor that can, among other things, create a detailed performance report about your PC, detail any system and performance issues, and suggest fixes.
To get the report, type perfmon /report into your search box and press Enter. (Make sure there’s a space between “perfmon” and the slash mark.) The Resource and Performance Monitor launches and gathers information about your system. It will say that it will take 60 seconds, but I’ve found that it takes several minutes. When the Monitor finishes, it will launch an interactive report.
You’ll find a lot of extremely detailed information in the report, and it can take a lot of time to go through. Your best bet is to first look at the Warnings section, which details the biggest issues (if any) it found on your PC, such as problems with Windows, with drivers and so on. It also tells you how to fix each problem — for example, how to turn on a device that has been disabled.
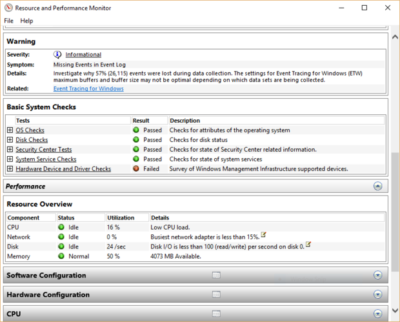
It is also worthwhile to scroll down to the Resource Overview section, where you’ll find an analysis of how well your CPU, network, disk and memory are performing. Each result is color-coded, with green meaning no problems, yellow meaning potential issues, and red showing a problem.
Beyond that, the Resource Overview also reports performance metrics and explanatory details. For example, for the CPU, it might show green and a utilization of 21%, with the details, “Normal CPU load.” Or for Memory, it might show yellow, with 62% utilization and the details, “1520 MB is available.” Based on what you get, you might want to do something about your hardware — for example, add more memory.
9. Kill bloatware
Sometimes the biggest factor slowing down your PC isn’t Windows 10 itself, but bloatware or adware that takes up CPU and system resources. Adware and bloatware are particularly insidious because they may have been installed by your computer’s manufacturer. You’d be amazed at how much more quickly your Windows 10 PC can run if you get rid of it.
First, run a system scan to find adware and malware. If you’ve already installed a security suite such as Norton Security or McAfee LiveSafe, you can use that. You can also use Windows 10’s built in anti-malware app — just type Windows Defender in the search box, press Enter, and then click Scan Now. Windows Defender will look for malware and remove any it finds.
It’s a good idea to get a second opinion, though, so consider a free tool like Malwarebytes Anti-Malware. The free version scans for malware and removes what it finds; the paid version offers always-on protection to stop infections in the first place.
Now you can check for bloatware and get rid of it. Several free programs will do this for you; your best bet is to run several of them, because no single one will find all the bloatware on your PC. Good choices are the PC Decrapifier, Should I Remove It? and SlimComputer.
10. Shut down and restart Windows
Here’s one of IT’s not-quite-secret weapons for troubleshooting and speeding up a PC: Shut it down and restart it. Doing that clears out any excess use of RAM that otherwise can’t be cleared. It also kills processes that you might have set in motion and are no longer needed, but that continue running and slow your system. If your Windows 10 PC has turned sluggish over time for no apparent reason, you may be surprised at how much more quickly it will run when you do this.
Try just some of these tricks, and you’ll find that you’ve got a faster Windows 10 PC — and one that is less likely to have any reliability problems.