Update 8/16/16: The Windows 10 Anniversary Update has begun rolling out for Windows 10 Mobile. The Anniversary Update includes additional features and improvements for your Windows 10 phone. To manually check for the update, on Start, swipe over to the All apps list, then select Settings > Update & security > Phone update > Check for updates. Note that availability may vary by manufacturer, model, country or region, mobile operator or service provider, hardware limitations and other factors.
The Windows 10 Anniversary Update has begun rolling out for customers around the world*. The Windows 10 Anniversary Update is full of new features and innovations that bring Windows Ink and Cortana** to life; a faster, more accessible and more power-efficient Microsoft Edge browser; advanced security features; new gaming experiences and more. The Windows 10 Anniversary Update will start rolling out to Windows 10 Mobile phones in the coming weeks.
The Windows 10 Anniversary Update is being rolled out to Windows 10 PCs across the world in phases starting with the newer machines first. You don’t have to do anything to get the Windows 10 Anniversary Update, it will roll out automatically to you through Windows Update if you’ve chosen to have updates installed automatically on your device. However, if you don’t want to wait for the update to roll out to you, you can manually get the update yourself on your personal PC. If you’re using a Windows 10 PC at work, you will need to check with your IT administrator for details on your organization’s specific plans to update.
Here are a couple ways you can manually get the Windows 10 Anniversary Update
Go to Settings > Updates & Security > Windows Update
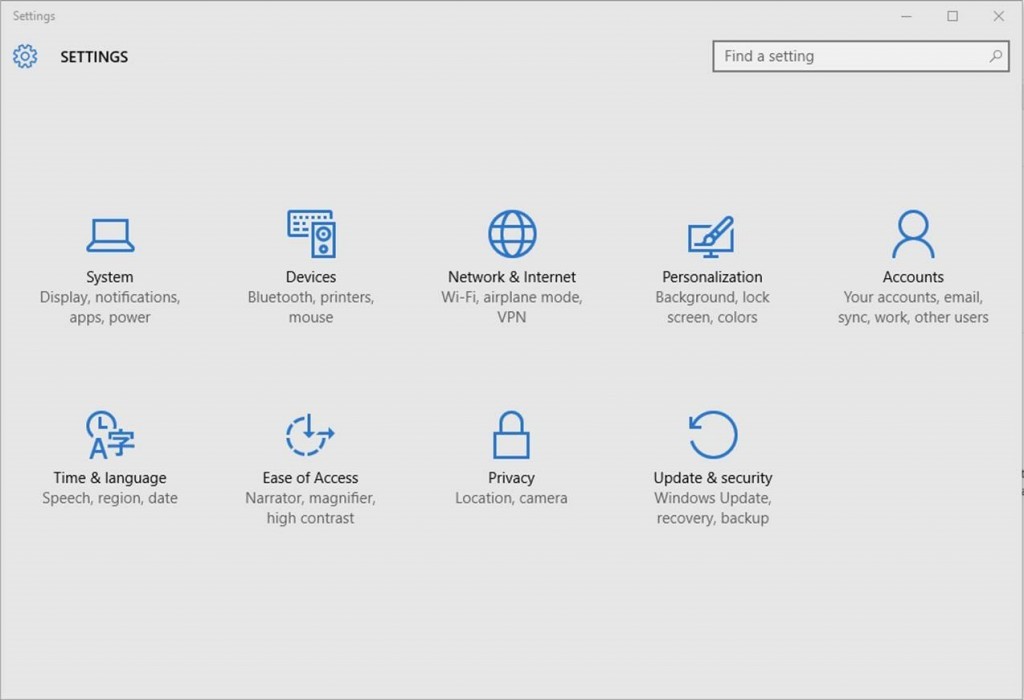
1. In Windows Update simply click Check for Updates.
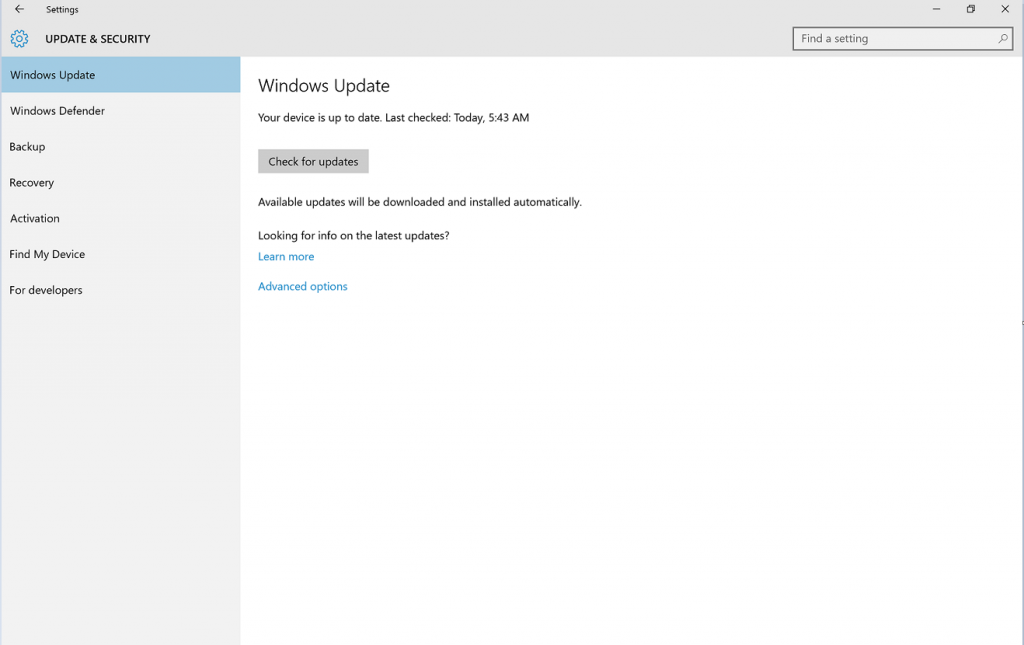
2. The Anniversary Update will appear as, Feature update to Windows 10, version 1607. Click update and the update will begin downloading and installing.
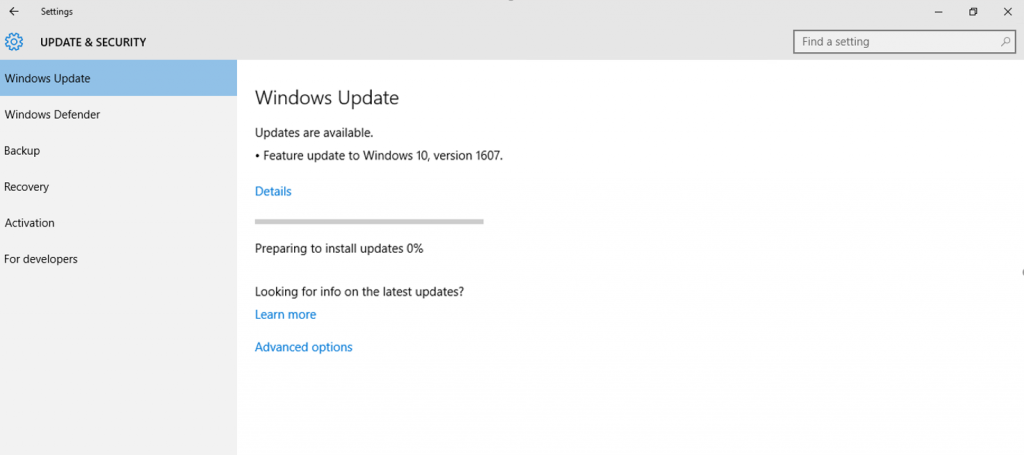
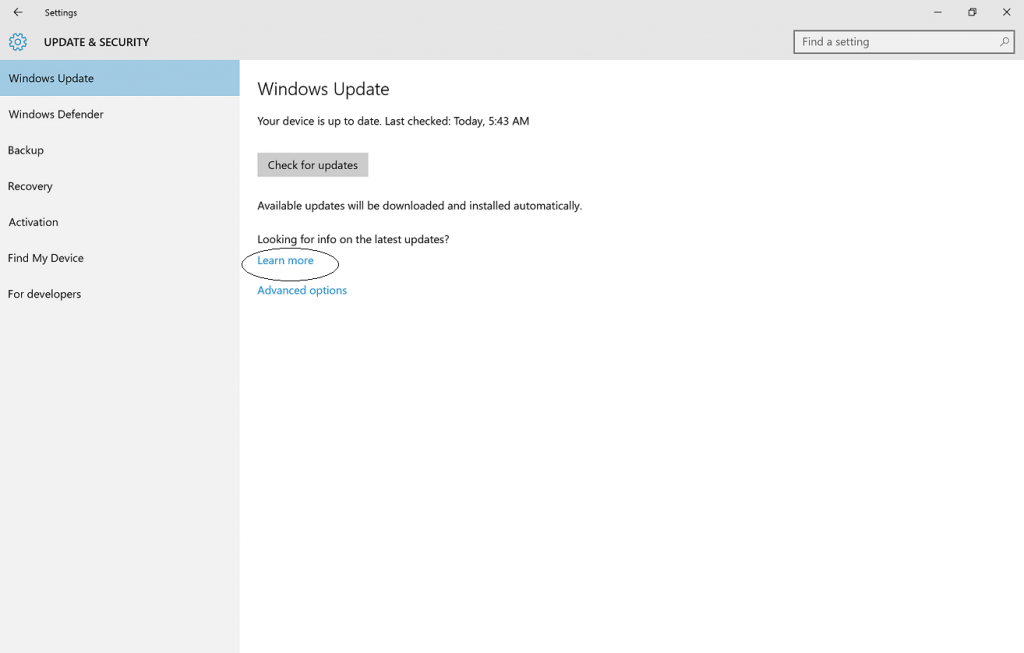
Another way to get the Windows 10 Anniversary Update will be by clicking “Learn more” just below the “Looking for info on the latest updates? In Windows Update.
From there you’ll be taken to a support page on Microsoft.com that will allow you to download the ISO file to your PC.
We hope you enjoy the Windows 10 Anniversary Update!
*Windows 10 Anniversary Update will be available in all countries where Windows 10 is available.
**Cortana available in select markets
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsoft’s Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.