Here’s how to clear the Address Resolution Protocol cache and how to manage that cache with a few command switches.

The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache is a crucial component of IP networking on any operating system. What ARP does is link Ethernet addressing (IP addressing) to hardware addressing (MAC addressing). Without this system, a machine could not communicate to the outside world as one addressing scheme could not communicate with the other.
The ARP Cache is a collection of ARP entries (mostly dynamic) that are created when a hostname is resolved to an IP address and then an IP address is resolved to a MAC address (so the computer can effectively communicate with the IP address).
When this happens, the PC will store that newly mapped address in the ARP cache, and it will stay there until the ARP cache entry timeout expires. This isn’t usually a problem, but sometimes a bad ARP entry can cause issues with Internet connections and Web page loading. When this occurs, one step that can be taken toward resolution is to clear the ARP cache. Yes, this means the ARP cache has to be rebuilt, which means a little more work for the PC, but that cache will rebuild fairly quickly.
Clearing the ARP cache is done completely through the command line, so stretch out those fingers and get ready to type. After we show you how to clear the ARP cache, we will show you how to manage that cache with a few command switches.
Flush the cache
Step 1: Open the command prompt
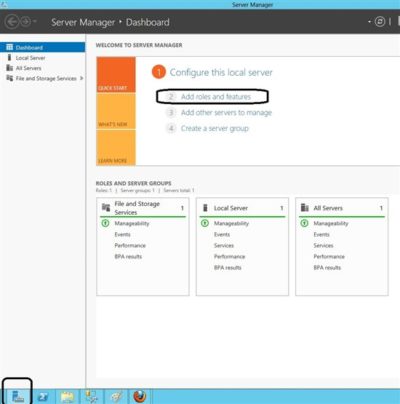
Click Start and then type “cmd” (no quotes) in the search dialog box, but don’t hit Enter yet. Right-click the cmd.exe icon and select Run as Administrator (Figure A). After answering the UAC, the terminal window will open offering up the command prompt.
Figure A
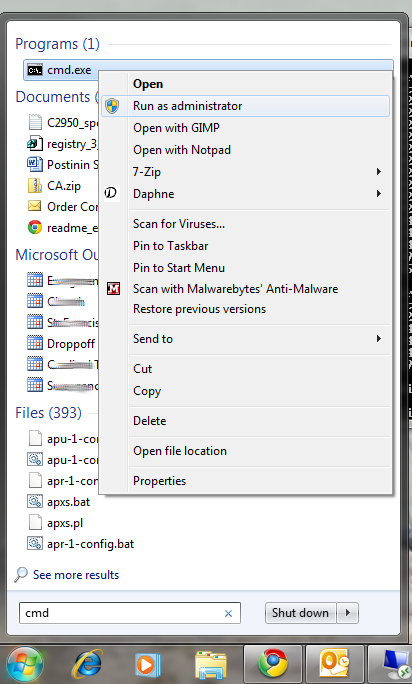
If the icon is already pinned in the Start menu, entering cmd is not necessary.
Step 2: Run the commands
The first command to run is
arp -a
This command will display all your ARP entries (Figure B). Naturally the -a option is not the only option available. The arp command also allows for the following switches:
| -d | Delete an IP address (arp -d 192.168.100.10) |
| -d -a | Delete all entries in the ARP table |
| -s | Add an entry to the ARP table (arp -s ADDRESS MAC_ADDRESS – Where ADDRESS is the address to be added and MAC_ADDRESS is the MAC address of the machine) |
Figure B
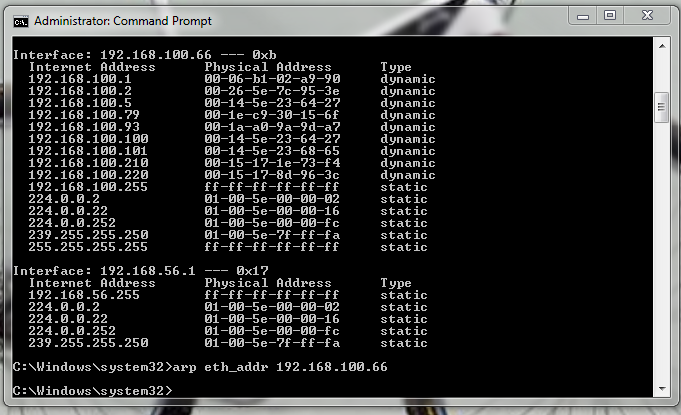
Here you see the arp cache for two different interfaces on a single machine.
To flush the entire cache, issue the following command:
netsh interface ip delete arpcache
The above command will flush the entire ARP cache on your system. Now as soon as network connections are made, the ARP cache will begin to repopulate.
Verify the flush
Once you have flushed the ARP cache, make sure to issue the command arp -a to see if the cache has, in fact, been flushed. If it does not flush, it could be the system is a victim of a Windows bug caused when Routing and Remote Services is enabled. This is a simple bug to fix:
1. Click Start | Control Panel.
2. Click Administrative Tools.
3. Click Computer Management.
4. Double-click Services and Applications.
5. Double-click Services.
6. Scroll down to Routing and Remote Services.
7. Double-click Routing and Remote Services.
8. Set the Startup Type to Disable.
9. Make sure the service is stopped.
Now try flushing the ARP cache again. It should work this time.
Troubleshooting
It is also possible to troubleshoot network connections using the ARP cache. For example, it is important to look out for invalid ARP entries that go to a MAC address of 00-00-00-00-00-00. If one such entry shows up, make sure to delete it from the cache using the -d switch. Say you have an ARP entry that looks like:
224.0.0.24 00-00-00-00-00-00 static
In order to delete this entry, use the arp command like so:
arp -d 224.0.0.24
And that invalid entry will be gone.
Final thoughts
There are so many ways to troubleshoot networking connections. Flushing the ARP cache is just one of those methods that is rarely thought of, but when all else fails this might be the last-gasp effort that makes you the hero of the day.
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsofts Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.