Where do you draw the line on personal privacy? The right options are different for everyone. This guide shows the privacy settings that will help you to create the right balance of privacy and convenience in Windows 10.

Over the past year, We’ve read countless “privacy guides” for Windows 10. Most are well-intentioned, but they invariably take a simplistic approach to privacy: Just turn off every switch in the Privacy section of the Settings app.
If you do that, you’re not understanding the privacy landscape, which encompasses far more than just those settings. You’re also missing some important additional steps.
Windows 10 is a mix of software and services. With every session, a Windows 10 device exchanges a great deal of information with Microsoft’s servers. That’s neither unusual nor alarming. Microsoft’s chief rivals, Google and Apple, are also blending services into their software, with the goal of making your life easier and making that software more reliable.
So are other tech companies that you don’t think of as software companies: Amazon, with the Echo. Tesla, with its self-updating, software-driven cars. Your thermostat and your home security system.
There’s something profoundly satisfying about a service that anticipates your every move, reminding you when to leave for an appointment to arrive on time, or to pick up flowers for your anniversary tomorrow. Your digital personal assistant, whether it’s Siri or Cortana or Alexa or Google, needs to be able to see your calendar and contacts to make that magic happen.
But when that sort of personal attention goes too far, it “crosses the creepy line,” to use a phrase that Eric Schmidt probably regrets uttering when he was Google’s CEO.
The thing about that line is that it’s drawn in a different place for everyone. There are people who are thrilled at the idea that their PC or mobile device is so familiar with their actions that it can anticipate what they’ll do next. I know others who would like to build a virtual Faraday cage around their computing hardware so that none of their personal details can escape.
Both of those viewpoints, and everything in between, are perfectly valid. That’s why the software and services we use are loaded with switches and dials designed to help you take control of their potential privacy impact.
In this post, We’ll walk you through the big privacy questions for Windows 10, with enough context to help you decide which settings are right for you.
Note that this guide assumes you are using Windows 10 on a personal PC or one in your small business. If you are in an enterprise setting, or if you are in a regulated industry, you should seek professional assistance to ensure that you’re meeting proper standards.
Let’s start with the part of your PC that has the biggest impact on your personal privacy.
THE NETWORK
No one knows more about your online identity than your Internet service provider. Every packet you send or receive from anywhere online goes through their servers. When you travel and connect to Wi-Fi networks that are under the control of others, the owners of those networks can see every connection you make and can intercept their contents.
Regardless of the platform you use, that’s why it’s important you use encrypted connections for any kind of sensitive communications. Using a virtual private network whenever possible is an excellent best practice.
Windows 10 does offer one obscure option that can help protect third parties from tracking your movements based on your connections to Wi-Fi networks. (Note that this feature requires support from your Wi-Fi adapter, so if you don’t see this option, the most likely explanation is that your hardware doesn’t support it.) Under Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi, turn the Use random hardware addresses setting to On.
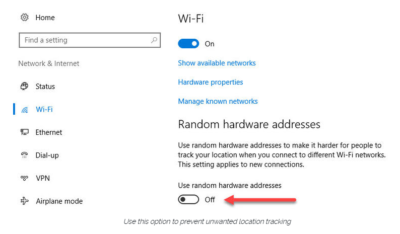
That step keeps third parties from matching your Wi-Fi adapter’s hardware address with your personal information, making it more difficult to track your location.
THE BROWSER
Countless third-party ad networks and analytics companies use cookies and other tracking technology to record your movements around the web and to correlate your online activities with your offline identity.
The result is a digital fingerprint that can be extraordinarily detailed and, unfortunately, outside of your ability to change.
To limit the amount of information that those ad and analytics companies know about you from your web browsing, consider third-party anti-tracking software such as Abine’s Blur, which is available for every web browser except Microsoft Edge. (That lack of solid support for add-ons is one reason I can’t yet recommend Edge as a full-time browser for most Windows 10 users.)
Another privacy product worth considering is Ghostery, although some are suspicious of this browser extension because of its uncomfortably close ties to the online advertising industry.
Ad-blocking software can also provide some privacy protection as a side-effect of performing its basic function. Here, too, watch out for close ties between some ad-blocking add-ins and the third-party trackers they supposedly protect you from.
Note that none of these steps is unique to Windows 10. Anti-tracking software is typically a browser add-in and works with most popular browsers.
THE OPERATING SYSTEM
With those two big, platform-independent factors out of the way, we can now turn to Windows 10 itself. When you use a Windows 10 device, it is capable of sharing the following types of information with Microsoft’s servers:
Your location
Windows 10 can determine your location to help with actions like automatically setting your current time zone. It can also record a location history on a per-device basis. Go to Settings > Privacy > Location to control the following:
- Location on/off?Use the master switch at the top of this page to disable all location features for all users of the current device.
- Location service on/off?If location is on for Windows, you can still turn it off for your user account here.
- General location?This allows you to set a city, zip code, or region so that apps can deliver relevant content.
- Default location?Click Set default to open the Maps app and specify the location you want Windows to use when a more precise location is not available.
- Location history?Click Clear to erase the saved history for a Windows 10 device.
If location is on, a list at the bottom of the Settings > Privacy > Location page allows you to disable access to that data on a per-app basis.
Your input
If you enable Cortana, Windows 10 uploads some info from your devices, such as your calendar, contacts, and location and browsing history, so that Cortana can make personalized recommendations. If you don’t want any accounts on your PC to use Cortana, follow the steps in this article to disable the feature completely: Turn off Cortana completely.
Windows 10 uses some feedback from the way you type, write, and speak to improve performance for you and as a way to improve the overall platform. This isn’t keystroke logging; rather, the operating system uses a very small amount of information. A separate feature uses your speech and writing history to make better suggestions in Windows and Cortana.
You can control this collection with two sets of controls:
Under Settings > Privacy > General, click Info about how I write and turn it off so that your typos aren’t used to improve things like the built-in spell checker.
Under Settings > Privacy > Speech, inking, & typing, under the Getting to know you heading, click Stop getting to know me to turn off personalization.
To clear previously saved information associated with your Microsoft account, click the first link under the Manage cloud info heading. That takes you to this Bing Personalization page, which includes this prominent button:
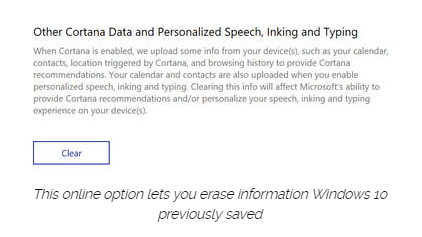
Click Clear to remove that saved information from the cloud.
Files and settings
When you sign in with a Microsoft account, you have the option to save files to the cloud using OneDrive. Windows 10 also syncs some settings to OneDrive, allowing you to have the same desktop background, saved passwords, and other personalized settings when you sign in with that account on multiple PCs.
If you use a local account, of course, none of your settings are synced. If you use a Microsoft account, you can turn off syncing completely or remove certain settings from the sync list by going to Settings > Accounts > Sync Your Settings.
OneDrive is an opt-in service. If you don’t sign in, it does nothing. You can’t save files to OneDrive accidentally, and no files are uploaded without your explicit permission, which you can revoke any time. To disable OneDrive for all users on your PC, follow these instructions: Shut down OneDrive completely.
Telemetry
Microsoft, like all modern software companies, uses feedback from its installed base to identify problems and improve performance. In Windows 10, this feedback mechanism produces diagnostics data (aka telemetry) that is uploaded to Microsoft at regular intervals. The data is anonymized and is not used to create a profile of you.
The default telemetry setting for all consumer and small business versions of Windows 10 is Full, which means that the uploaded data also includes details (also anonymized) about app usage. If you are concerned about possible inadvertent leakage of personal information, I recommend that you go to Settings > Privacy > Feedback & diagnostics and change the Diagnostic and usage data setting to Basic.
THE APPS
Although the number of subcategories under the Privacy heading in Settings seems daunting, most of them govern access to your information by Windows Store apps. That set of apps includes those that are preinstalled (Mail, Calendar, Groove Music, Photos, and so on) as well as those you acquire from the Store.
Most of the categories offer a single on-off switch at the top, which you can use to disable all access to that feature by all apps. If you leave the feature enabled, you can use a list of apps at the bottom of the page to enable or disable access on a per-app basis.
This capability works the same with the following categories: Camera, Microphone, Notifications, Account Info, Call History, and Radios. The Other Devices category lets apps automatically share and sync info with wireless devices that aren’t explicitly paired with your PC. Use the Background Apps category to specify which apps are allowed to work in the background.
If Location is enabled, you have the option to disable location access on a per-app basis and to disable Geofencing.
The Contacts, Calendar, Email, and Messaging categories allow you to control which apps can have access to these features. If you want to share content from an app using email or messaging, this option has to be on for that app. Note that Mail and Calendar, People, and Phone always have access to your contacts; Mail and Calendar are always allowed to access and send email and always have access to your calendar.
Finally, one horribly misunderstood setting is available under Settings > Privacy > General. Advertising ID controls whether Microsoft serves personalized ads to ad-supported apps. If you turn this option off, you still get ads, but they’re not personalized. In any case, your information is not shared with advertisers.
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsofts Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.