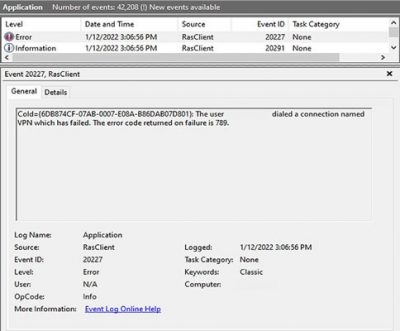
Sling TV CEO Roger Lynch talks pricing, DVR, and certified hardware.
A lot’s changed in the two years since Sling TV made its grand debut at CES 2015. Instead of being the only streaming option for cable channels like ESPN and CNN, Sling is now one of three options alongside PlayStation Vue and DirecTV Now, and it will soon have a fourth competitor in Hulu.
Accordingly, Sling has changed with the times. The company, a subsidiary of Dish Network, has added new channels, created a second base package with a different mix of channels, and is working on a cloud DVR feature.
What else is in store for Sling this year? Here’s what we learned from Roger Lynch, Sling’s CEO, during CES 2017:
On DVR, which is “months” away
Sling began testing DVR service in an invite-only beta on Roku devices last month, and while it’s clearly a work in progress, Lynch says feedback has been positive. “The only feedback that isn’t positive is, ‘I wish I had this feature or that feature,’ all of which are being built already anyway,” Lynch says.
For now, Sling is prioritizing simple improvements like grouping recordings from a series into a folder, rather than listing them all separately. The eventual goal is to list all episodes from a series—whether it’s on-demand, recorded, or live—in a single window.
Still, Lynch gave only a rough time frame for when DVR might launch publicly, “It’s not in weeks. It’s not in years. It’s in months,” he says. “We want to get it out as quickly as possible.”
On AirTV and “Optimized for Sling TV”
Just before CES began, Dish announced a new brand called AirTV. Its first product, the AirTV player, puts Sling TV front-and-center, while integrating over-the-air channels and Netflix recommendations into the Sling guide.
Lynch sees AirTV as an example for other device makers to follow. “I’m hopeful that other device partners will make devices similar to this, and do similar types of integrations for Sling, and that it’ll spur innovation in the ecosystem,” he says.

To that end, Sling’s sole CES announcement was an “Optimized for Sling TV” certification program, which will help consumers know whether a device works well with the service. With streaming devices, for instance, criteria could include a Sling button on the remote control, integration with over-the-air broadcasts in the Sling guide, and a way to auto-launch Sling when users turn on the device.
Lynch says Sling is still finalizing how it’ll enforce those criteria. Roku, for instance, pre-loads the Sling app and includes a quick-launch remote button on some models, and that might be enough to earn Sling’s approval. Other types of devices may have different criteria.
“There’s router companies that are looking to be optimized for Sling. So what does that mean for router companies? It doesn’t meant they’re going to integrate OTA and put a button on the remote. It means they’re going to do something to optimize for the experience,” Lynch says.
On separating Sling Orange and Blue
Last year, Sling introduced a second base package, separate from its original $20-per-month plan. The newer plan is called Sling Blue, and it starts at $25 per month, while the original is now called Sling Orange. (Subscribers can bundle the two plans, which have different channel lineups with some overlap, for $40 per month.)
Might Sling eventually try to merge these two plans?
“We work really, really hard not to combine them,” Lynch says. “The problem with combining them is, you end up with a $35 to $40 package because there’s so much content, and you price yourself out of the market from where I think the big opportunities [are].”
That sounds like a shot at rivals like PlayStation Vue, DirecTV Now, and Hulu, none of whom are attempting to match Sling’s base prices. “For us, the Sling Orange product is the perfect cord-cutter product. It’s great for people who use antennas because you’re not forced to buy locals, and locals are really expensive,” Lynch says.
Sling Blue, meanwhile, will likely compete more directly with those larger bundles over time. “That’ll become a broader content package at a higher price point,” Lynch says.
On getting what it wants from TV networks
Since its launch in 2015, Sling has offered a “Replay” feature that lets users rewind live TV and watch several days’ worth of past programming. It’s a nice alternative to setting up a DVR, but not every channel supports the feature.
As you might expect, that’s partly because of issues with streaming rights. But Sling is working on accommodating those issues so it can support Replay on more channels.
“Every program has different requirements, like, can you fast forward, can you not fast forward, yes you can fast forward, but not through commercials,” Lynch says. “There are channels that have granted us rights to Replay, but we haven’t made Replay available on the channel yet, because we still have to put in some technology to enable that, because of the business rules that channel has.”

On the whole, though, negotiating those sorts of features with TV networks is getting easier. Lynch notes that two years ago, Sling was scrambling just to get a basic package together—the service launched with a mere 11 channels—but now TV networks are much more interested.
“When we first launched,” Lynch says, “we didn’t have as much leverage to demand things like that as we do now.”
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsofts Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.